|
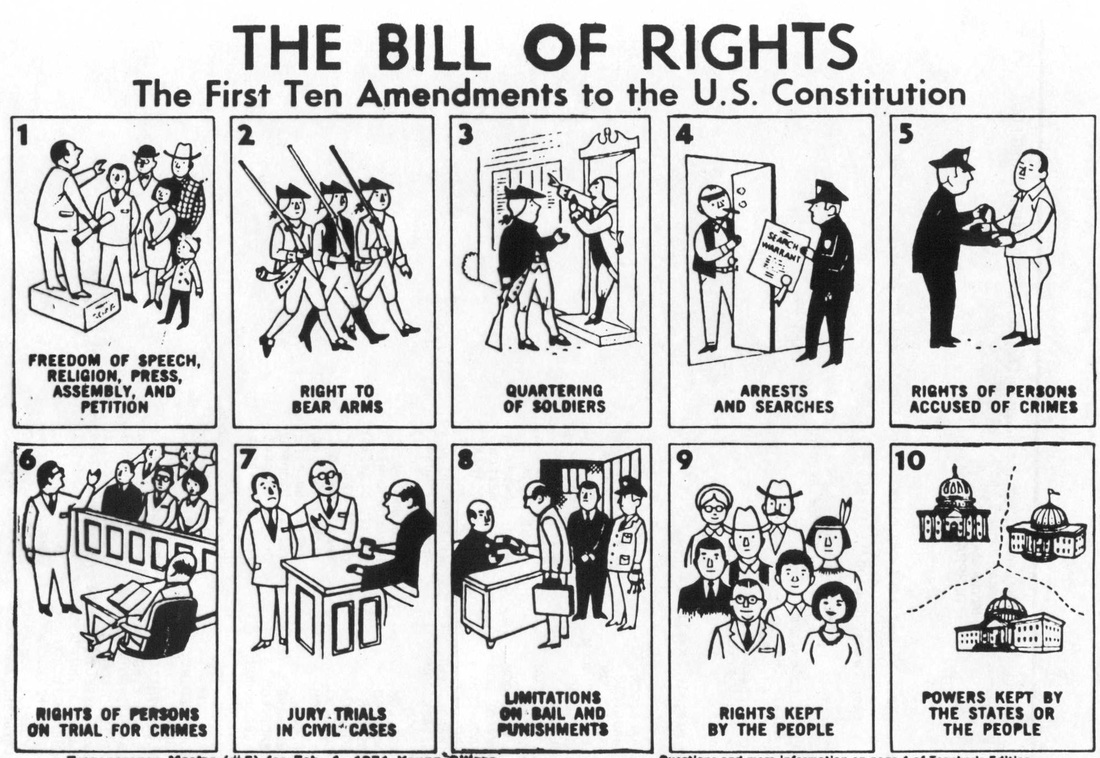
The United States Constitution has 27 Amendments. The first 10 Amendments to the Constitution are called the Bill of Rights.The Bill of Rights was ratified, or approved, in 1791. It outlines the basic rights and freedoms of American citizens.
Amendment 1 The First Amendment protects the rights of every American. It defines the freedoms of religion, speech, and press. Most Americans believe that the First Amendment guarantees their most important rights. Amendment 2 The Second Amendment guarantees Americans the right to bear arms, or own guns. Amendment 3 The Third Amendment prevents the government from forcing citizens to shelter soldiers in their homes. Amendment 4 The Fourth Amendment protects the privacy of American citizens. It prohibits, or prevents, unnecessary or unreasonable searches of a person's property. Amendment 5 In the Fifth Amendment, all Americans are guaranteed the right to a fair and legal trial. It also protects someone from testifying against him- or herself under oath. Amendment 6 A right to a speedy trial is guaranteed in the Sixth Amendment. Amendment 7 The Seventh Amendment guarantees the right to a trial by jury in civil, or private, legal cases where damages are more than $20. Civil cases solve disputes between citizens. Amendment 8 Unreasonable bail or fines and cruel and unusual punishment are prohibited in the Eighth Amendment. Amendment 9 The Ninth Amendment recognizes that Americans have rights that are not listed in the Constitution. Amendment 10 The Tenth Amendment says that the powers not given to the United States government by the Constitution belong to the states or to the people. Other Amendments were added to the Constitution over the years, and more may be added later. The Constitution currently contains 27 amendments. Below are some of the highlights of the 17 Amendments added after the Bill of Rights was ratified. The Thirteenth Amendment became law in 1865. It makes slavery, and other forms of forced labor, illegal. Ratified in 1870, the Fifteenth Amendment stated that no citizen should be denied the right to vote on the basis of race or color. In 1920, the Nineteenth Amendment gave women the right to vote. |
AuthorJonathan St. Mary. ArchivesCategories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
